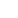Mechanical parts processing industry is a pillar industry of the national economy and has broad prospects. When machining fine mechanical parts in a machining plant, there are many requirements and regulations on the machining process to ensure the qualification rate of factory parts.
Remove the jaw of the vice, process two M4 threaded holes, flush two 1.5mm thick steel plates 2 with the jaw, rivet the 0.8mm thick hard brass plate 3 with aluminum countersunk rivets, and fasten it on the jaw with M4 countersunk screws 1 to form a durable soft jaw. This also protects the hardware parts from being clamped and is interchangeable.
For a workpiece, clamp it first and then locate it, because the workpiece deformation will be tried during clamping, so clamp it first and then locate it. For 6-point positioning, find the limit of its degrees of freedom. When the handle of the Allen wrench is short and the force cannot be concentrated, the wrench can insert a pipe with an inner diameter slightly larger than the wrench from the milling groove, which can be used as a long handle.
In the process of mechanical equipment manufacturing, machining deviation mainly includes spindle rotation deviation, guide rail deviation and transmission chain deviation. Spindle rotation deviation refers to the change of the actual rotation axis of the spindle relative to its average rotation axis at each moment, which directly affects the accuracy of the machined workpiece.
Machining manufacturer
The main root causes of spindle rotation deviation are spindle coaxiality deviation, bearing itself deviation, coaxiality deviation between bearings, spindle winding, etc. The guide rail is not only the benchmark for determining the relative position relationship of machine tool components on the machine tool, but also the benchmark for machine tool movement.
The manufacturing deviation, uneven wear and installation quality of the guide rail itself are important factors leading to the deviation of the guide rail. Transmission chain deviation refers to the relative motion deviation between the transmission elements at both ends of the transmission chain. It is caused by the manufacturing and assembly deviation of each component of the transmission chain and the wear in the process of use.
Machining experience points out that any tool will inevitably wear in the cutting process, resulting in the change of workpiece size and shape. The influence of tool geometric deviation on machining deviation varies with tool type: when using fixed size tools, the manufacturing deviation of tools will directly affect the machining accuracy of workpieces; For general cutting tools, the manufacturing deviation has no direct impact on the machining deviation.
The function of fixture is to make the workpiece equivalent to the correct position of tool and machine tool, so the geometric deviation of fixture has a great impact on machining deviation (especially position deviation). The thermal deformation of the process system has a great influence on the machining deviation, especially in static processing and large workpiece processing, the machining deviation caused by thermal deformation sometimes accounts for 50% of the total deviation of the workpiece.
Post time: Nov-09-2021